
(Explore the role of DBAs, or database administrators.) DBMS system schematic Furthermore, they allow organizations to have a governable top-down view of all the data, users, groups, locations, etc., in an organized manner. Most modern DBMS support handling multiple database workloads from a centralized DBMS software, even in a distributed database scenario. In a recovery operation, DBMS provides a recovery platform with the necessary tools to fully or partially restore databases to their previous state-effortlessly.Īll these administrative tasks are facilitated using a single management interface. It reduces I/O usage to optimize SQL queries, enabling the best performance from the database. DBMS can monitor the performance of databases using integrated tools and enable users to tune databases by creating optimized indexes. They can even move these backups to third-party locations such as cloud storage for safekeeping. DBMS can simplify the backup process of databases by providing a simpler and straightforward interface to manage backups and snapshots. These operations allow administrators to limit access to underlying data, control user actions, and manage users in databases. Easily configure user accounts, define access policies, modify restrictions, and access scopes. Configuring authentication and authorization.The typical database administrative tasks that can be performed using a DBMS include: These actions can range from simply querying data to defining database schemas that fundamentally affect the database structure.įurthermore, DBMS allow users to interact with a database securely and concurrently without interfering with each user and while maintaining data integrity. It allows users to access and interact with the underlying data in the database.
#Easy relational database software software
What is a database management system?Ī database management system (DBMS) is a software tool that enables users to manage a database easily. This is where database management systems come into play-by offering a platform to manage databases. As a result, organizations require robust, secure, and user-friendly tools to maintain these databases. When this is coupled with compliance requirements and the distributed nature of most data sets, managing databases has become highly complex.
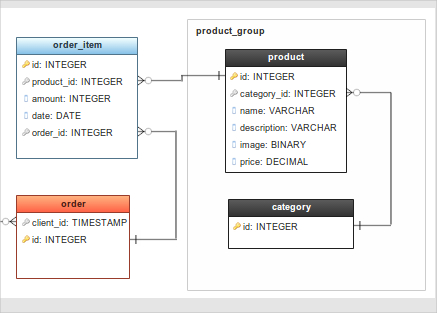
On top of that, databases are continuously handling mission-critical and sensitive data. Each type has the ability to handle structured, semi-structured, and even unstructured data. With the explosion of web and cloud technologies, databases have evolved from traditional relational databases to more advanced types of databases such as NoSQL, columnar, key-value, hierarchical, and distributed databases.

Data is the cornerstone of any modern software application, and databases are the most common way to store and manage data used by applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
